I like the WS2812 Neopixel boards, modules and LEDs you can buy and have been looking at some of the variants but coming at over $35 for some of these I baulked at buying them, recently I found compatible boards for a fraction of the price and decided to but them. The first is an WS2812 8×8 64 LED Matrix LED 5050 module
Warning : Each LED is capable of drawing as much as 60mA (at peak brightness the matrix can draw just over 3.5 Amps at 5 Volts), this adds up so it is suggested to use a 5V 2A power supply. For most uses, you’ll see about 1-2A of current per panel. I tend to use the lower values in the code examples you will see later
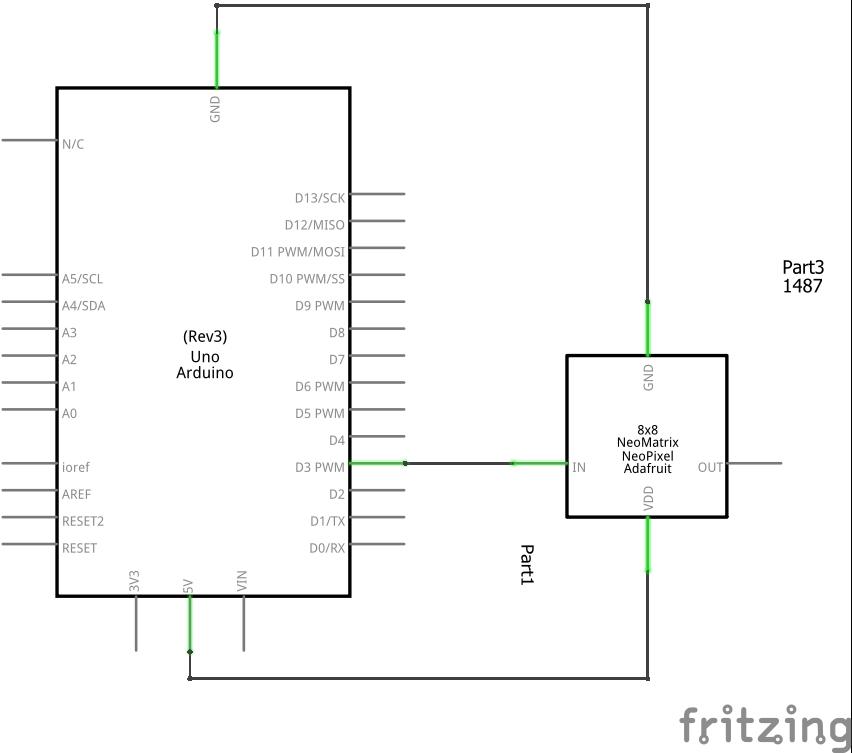
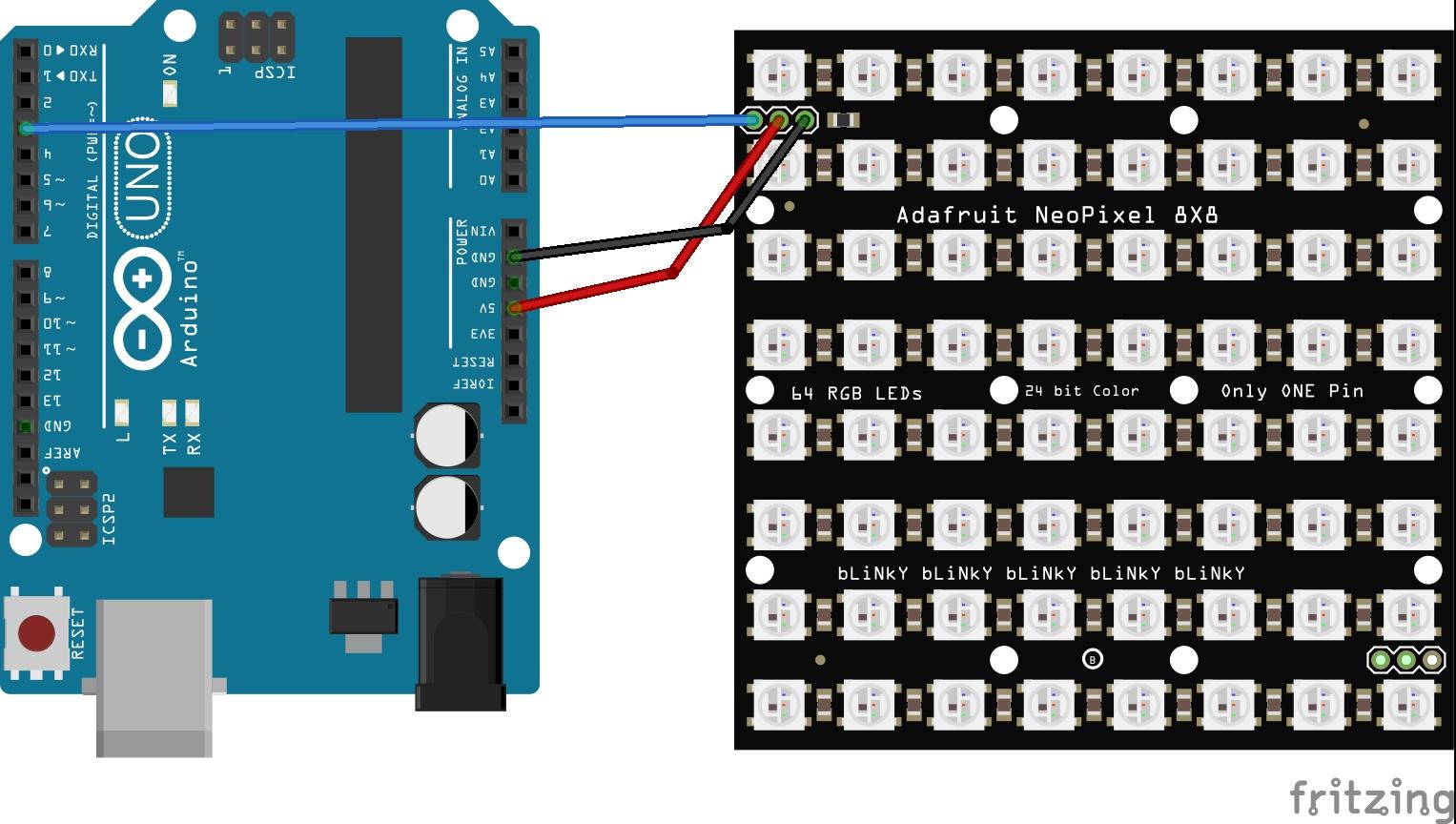
Solder wires or a header to the input port and supply power to the +5V and ground pins, then connect the DIN pin to a pin of your microcontroller
Schematics/Layout
Code Examples
Example 1
[codesyntax lang=”cpp”]
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
// Which pin on the Arduino is connected to the NeoPixels?
// On a Trinket or Gemma we suggest changing this to 1
#define PIN 3
// How many NeoPixels are attached to the Arduino?
#define NUMPIXELS 64
Adafruit_NeoPixel pixels = Adafruit_NeoPixel(NUMPIXELS, PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
int delayval = 10; // delay for half a second
void setup()
{
pixels.begin(); // This initializes the NeoPixel library.
}
void loop() {
// For a set of NeoPixels the first NeoPixel is 0, second is 1, all the way up to the count of pixels minus one.
for(int i=0;i<NUMPIXELS;i++)
{
// pixels.Color takes RGB values, from 0,0,0 up to 255,255,255
pixels.setPixelColor(i, pixels.Color(1,0,0)); // Moderately bright green color.
pixels.show(); // This sends the updated pixel color to the hardware.
//delay(delayval);
}
delay(1000);
for(int i=0;i<NUMPIXELS;i++)
{
// pixels.Color takes RGB values, from 0,0,0 up to 255,255,255
pixels.setPixelColor(i, pixels.Color(0,1,0)); // Moderately bright green color.
pixels.show(); // This sends the updated pixel color to the hardware.
//delay(delayval);
}
delay(1000);
for(int i=0;i<NUMPIXELS;i++)
{
// pixels.Color takes RGB values, from 0,0,0 up to 255,255,255
pixels.setPixelColor(i, pixels.Color(0,0,1)); // Moderately bright green color.
pixels.show(); // This sends the updated pixel color to the hardware.
//delay(delayval);
}
delay(1000);
}
[/codesyntax]
Example 2
[codesyntax lang=”cpp”]
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
// Which pin on the Arduino is connected to the NeoPixels?
// On a Trinket or Gemma we suggest changing this to 1
#define PIN 3
// How many NeoPixels are attached to the Arduino?
#define NUMPIXELS 64
Adafruit_NeoPixel pixels = Adafruit_NeoPixel(NUMPIXELS, PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
int delayval = 10; // delay for half a second
void setup()
{
pixels.begin(); // This initializes the NeoPixel library.
}
void loop() {
// For a set of NeoPixels the first NeoPixel is 0, second is 1, all the way up to the count of pixels minus one.
for(int i=0;i<16;i++)
{
// pixels.Color takes RGB values, from 0,0,0 up to 255,255,255
pixels.setPixelColor(i, pixels.Color(1,0,0)); // Moderately bright green color.
pixels.show(); // This sends the updated pixel color to the hardware.
//delay(delayval);
}
//delay(1000);
for(int i=16;i<32;i++)
{
// pixels.Color takes RGB values, from 0,0,0 up to 255,255,255
pixels.setPixelColor(i, pixels.Color(0,1,0)); // Moderately bright green color.
pixels.show(); // This sends the updated pixel color to the hardware.
//delay(delayval);
}
//delay(1000);
for(int i=32;i<64;i++)
{
// pixels.Color takes RGB values, from 0,0,0 up to 255,255,255
pixels.setPixelColor(i, pixels.Color(0,0,1)); // Moderately bright green color.
pixels.show(); // This sends the updated pixel color to the hardware.
//delay(delayval);
}
//delay(1000);
}
[/codesyntax]
Example 3
[codesyntax lang=”cpp”]
include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
// Which pin on the Arduino is connected to the NeoPixels?
#define PIN 3
// How many NeoPixels are attached to the Arduino?
#define NUMPIXELS 64
Adafruit_NeoPixel pixels = Adafruit_NeoPixel(NUMPIXELS, PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
int delayval = 10; // delay for half a second
void setup()
{
pixels.begin(); // This initializes the NeoPixel library.
randomSeed(analogRead(0));
}
void loop() {
// For a set of NeoPixels the first NeoPixel is 0, second is 1, all the way up to the count of pixels minus one.
int rndRedValue = random(0,5);
int rndGreenValue = random(0,5);
int rndBlueValue = random(0,5);
for(int i=0;i<NUMPIXELS;i++)
{
// pixels.Color takes RGB values, from 0,0,0 up to 255,255,255
pixels.setPixelColor(i, pixels.Color(rndRedValue,rndGreenValue,rndBlueValue)); // Moderately bright green color.
pixels.show(); // This sends the updated pixel color to the hardware.
//delay(delayval);
}
delay(1000);
}
[/codesyntax]
Example 4
[codesyntax lang=”cpp”]
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
// Which pin on the Arduino is connected to the NeoPixels?
#define PIN 3
// How many NeoPixels are attached to the Arduino?
#define NUMPIXELS 64
Adafruit_NeoPixel pixels = Adafruit_NeoPixel(NUMPIXELS, PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
int delayval = 10; // delay for half a second
void setup()
{
pixels.begin(); // This initializes the NeoPixel library.
randomSeed(analogRead(0));
}
void loop() {
// For a set of NeoPixels the first NeoPixel is 0, second is 1, all the way up to the count of pixels minus one.
int rndRedValue = random(0,5);
int rndGreenValue = random(0,5);
int rndBlueValue = random(0,5);
int rndLED = random(0,64);
for(int i=0;i<rndLED;i++)
{
// pixels.Color takes RGB values, from 0,0,0 up to 255,255,255
pixels.setPixelColor(i, pixels.Color(rndRedValue,rndGreenValue,rndBlueValue)); // Moderately bright green color.
pixels.show(); // This sends the updated pixel color to the hardware.
//delay(delayval);
}
delay(1000);
}
[/codesyntax]
Links
WS2812 LED 5050 RGB 8×8 64 LED Matrix for Arduino