Freescale’s MAG3110 is a small, low-power, digital 3-axis magnetometer. The device can be used in conjunction with a 3-axis accelerometer to realize an orientation independent electronic compass that can provide accurate heading information. It features a standard I2C serial interface output and smart embedded functions.
The MAG3110 is capable of measuring magnetic fields with an output data rate (ODR) up to 80 Hz; these output data rates correspond to sample intervals from 12.5 ms to several seconds. The MAG3110 is available in a plastic DFN package and it is guaranteed to operate over the extended temperature range of -40°C to +85°C.
Again for ease to use its easier to buy a module with the device fitted to it, here is one that I purchased. You can see the MAG3110 in the middle of the picture
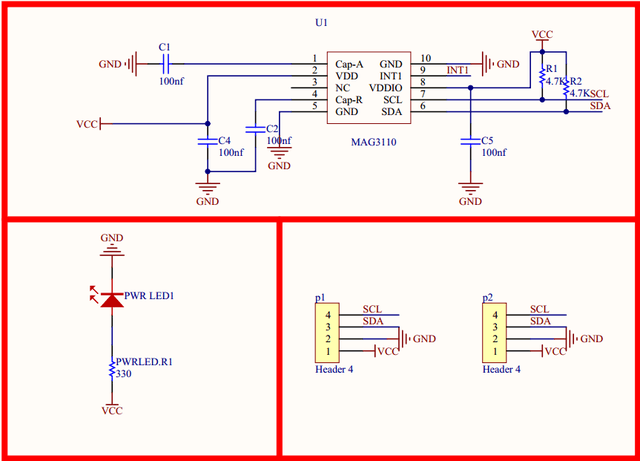
I also found this schematic online of a similar module to the one pictured above. Looking at the schematic it looks very similar to the module
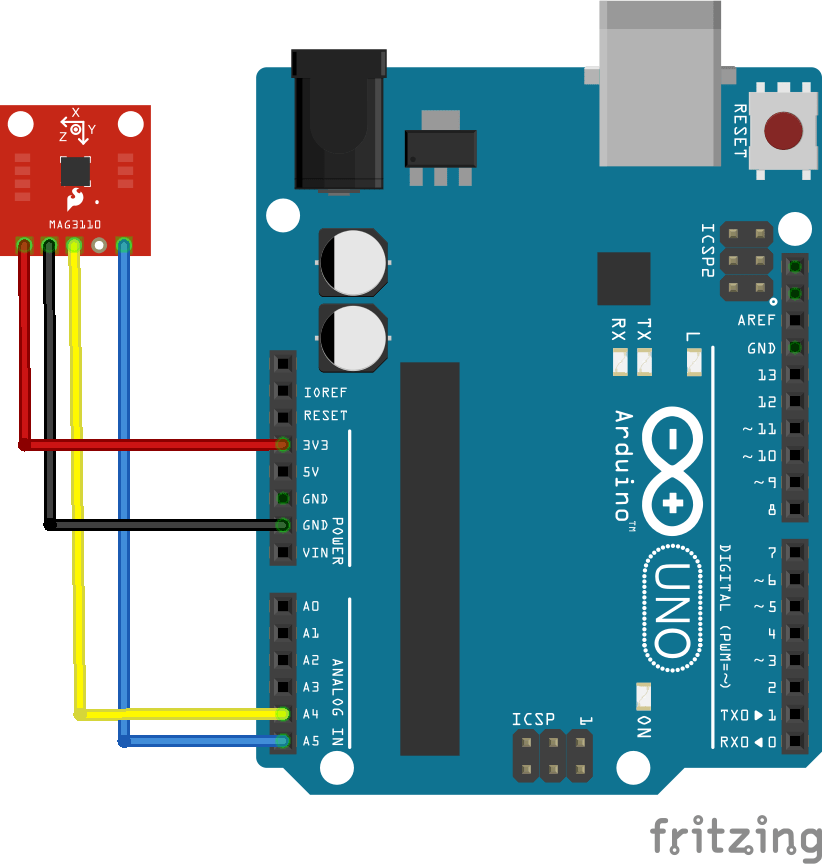
Connection
| Arduino Pin | MAG3110 Pin |
| 3v3 | VCC |
| GND | GND |
| D4 | SDA |
| D5 | SCL |
Layout
An I2C device so easy to wire up as per the connections above
Code
This particular code example does not require any libraries
[codesyntax lang=”cpp”]
#include <Wire.h>
#define MAG_ADDR 0x0E //7-bit address for the MAG3110, doesn't change
void setup()
{
Wire.begin(); // join i2c bus (address optional for master)
Serial.begin(9600); // start serial for output
config(); // turn the MAG3110 on
}
void loop()
{
print_values();
delay(5);
}
void config(void)
{
Wire.beginTransmission(MAG_ADDR); // transmit to device 0x0E
Wire.write(0x11); // cntrl register2
Wire.write(0x80); // write 0x80, enable auto resets
Wire.endTransmission(); // stop transmitting
delay(15);
Wire.beginTransmission(MAG_ADDR); // transmit to device 0x0E
Wire.write(0x10); // cntrl register1
Wire.write(1); // write 0x01, active mode
Wire.endTransmission(); // stop transmitting
}
void print_values(void)
{
Serial.print("x=");
Serial.print(read_x());
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print("y=");
Serial.print(read_y());
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print("z=");
Serial.println(read_z());
}
int mag_read_register(int reg)
{
int reg_val;
Wire.beginTransmission(MAG_ADDR); // transmit to device 0x0E
Wire.write(reg); // x MSB reg
Wire.endTransmission(); // stop transmitting
delayMicroseconds(2); //needs at least 1.3us free time between start and stop
Wire.requestFrom(MAG_ADDR, 1); // request 1 byte
while(Wire.available()) // slave may write less than requested
{
reg_val = Wire.read(); // read the byte
}
return reg_val;
}
int mag_read_value(int msb_reg, int lsb_reg)
{
int val_low, val_high; //define the MSB and LSB
val_high = mag_read_register(msb_reg);
delayMicroseconds(2); //needs at least 1.3us free time between start and stop
val_low = mag_read_register(lsb_reg);
int out = (val_low|(val_high << 8)); //concatenate the MSB and LSB
return out;
}
int read_x(void)
{
return mag_read_value(0x01, 0x02);
}
int read_y(void)
{
return mag_read_value(0x03, 0x04);
}
int read_z(void)
{
return mag_read_value(0x05, 0x06);
}
[/codesyntax]
Testing
Open up the serial monitor
x=44,y=1138,z=1505
x=65175,y=580,z=2037
x=65117,y=745,z=1435
x=65145,y=1487,z=1814
x=64700,y=949,z=1912
x=64848,y=671,z=1921
x=65411,y=803,z=2218
x=64852,y=720,z=1644