In this example we will connect a MMA8452Q accelerometer to an Arduino Uno
Lets look at some information about the sensor
The MMA8452Q is a smart, low-power, three-axis, capacitive, micromachined accelerometer with 12 bits of resolution. This accelerometer is packed with embedded functions with flexible user programmable options, configurable to two interrupt pins. Embedded interrupt functions allow for overall power savings relieving the host processor from continuously polling data.
The MMA8452Q has user selectable full scales of ±2 g/±4 g/±8 g with high-pass filtered data as well as non-filtered data available real-time. The device can be configured to generate inertial wakeup interrupt signals from any combination of the configurable embedded functions allowing the MMA8452Q to monitor events and remain in a low-power mode during periods of inactivity
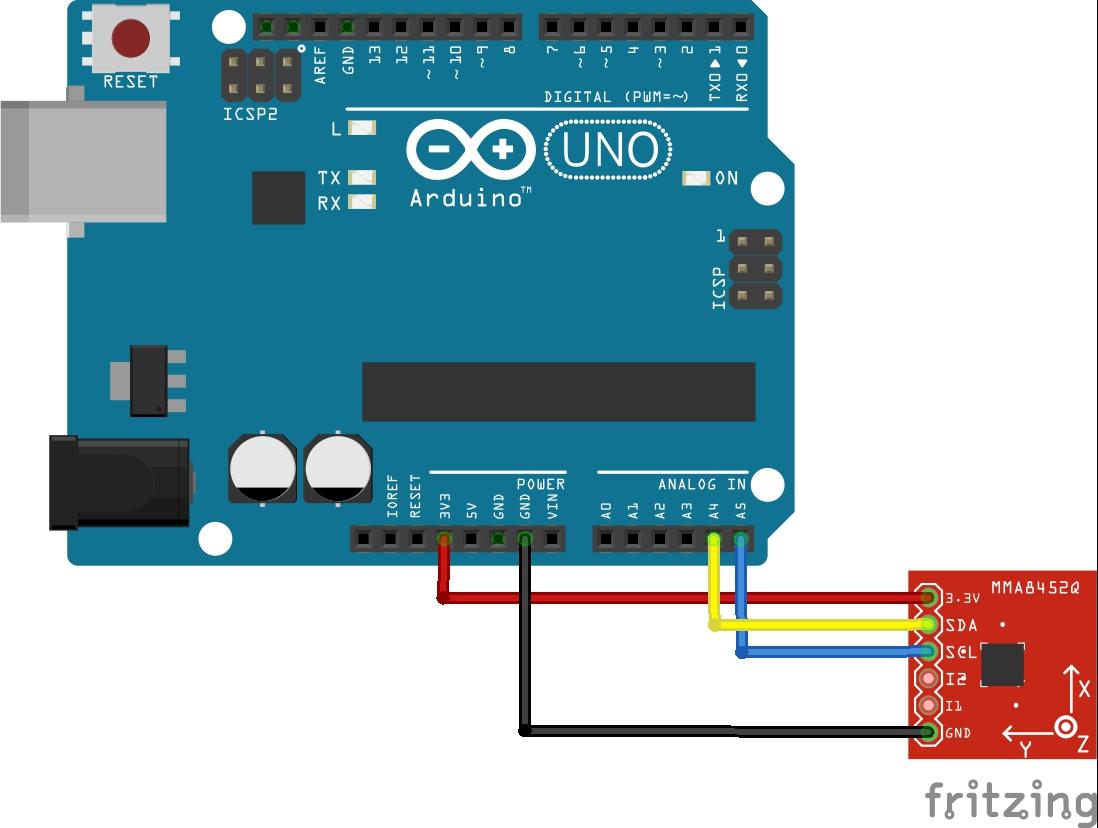
Connection
Here is a layout, its an easy device to connect
Parts List
Here are the parts I used
Code
There is a library from sparkfun but there is this example which does not require any libraries
[codesyntax lang=”cpp”]
// Distributed with a free-will license.
// Use it any way you want, profit or free, provided it fits in the licenses of its associated works.
// MMA8452Q
// This code is designed to work with the MMA8452Q_I2CS I2C Mini Module available from ControlEverything.com.
// https://www.controleverything.com/content/Accelorometer?sku=MMA8452Q_I2CS#tabs-0-product_tabset-2
#include <Wire.h>
// MMA8452Q I2C address is 0x1C(28)
#define Addr 0x1C
void setup()
{
// Initialise I2C communication as MASTER
Wire.begin();
// Initialise Serial Communication, set baud rate = 9600
Serial.begin(9600);
// Start I2C Transmission
Wire.beginTransmission(Addr);
// Select control register
Wire.write(0x2A);
// StandBy mode
Wire.write(0x00);
// Stop I2C Transmission
Wire.endTransmission();
// Start I2C Transmission
Wire.beginTransmission(Addr);
// Select control register
Wire.write(0x2A);
// Active mode
Wire.write(0x01);
// Stop I2C Transmission
Wire.endTransmission();
// Start I2C Transmission
Wire.beginTransmission(Addr);
// Select control register
Wire.write(0x0E);
// Set range to +/- 2g
Wire.write(0x00);
// Stop I2C Transmission
Wire.endTransmission();
delay(300);
}
void loop()
{
unsigned int data[7];
// Request 7 bytes of data
Wire.requestFrom(Addr, 7);
// Read 7 bytes of data
// staus, xAccl lsb, xAccl msb, yAccl lsb, yAccl msb, zAccl lsb, zAccl msb
if(Wire.available() == 7)
{
data[0] = Wire.read();
data[1] = Wire.read();
data[2] = Wire.read();
data[3] = Wire.read();
data[4] = Wire.read();
data[5] = Wire.read();
data[6] = Wire.read();
}
// Convert the data to 12-bits
int xAccl = ((data[1] * 256) + data[2]) / 16;
if (xAccl > 2047)
{
xAccl -= 4096;
}
int yAccl = ((data[3] * 256) + data[4]) / 16;
if (yAccl > 2047)
{
yAccl -= 4096;
}
int zAccl = ((data[5] * 256) + data[6]) / 16;
if (zAccl > 2047)
{
zAccl -= 4096;
}
// Output data to serial monitor
Serial.print("Acceleration in X-Axis : ");
Serial.println(xAccl);
Serial.print("Acceleration in Y-Axis : ");
Serial.println(yAccl);
Serial.print("Acceleration in Z-Axis : ");
Serial.println(zAccl);
delay(500);
}
[/codesyntax]
Output
Open the serial monitor – this is what you should expect to see
Acceleration in X-Axis : -186
Acceleration in Y-Axis : 330
Acceleration in Z-Axis : 125
Acceleration in X-Axis : -784
Acceleration in Y-Axis : 426
Acceleration in Z-Axis : 76
Acceleration in X-Axis : -225
Acceleration in Y-Axis : 890
Acceleration in Z-Axis : -273
Acceleration in X-Axis : -199
Acceleration in Y-Axis : 1053
Acceleration in Z-Axis : -260
Links
https://www.nxp.com/docs/en/data-sheet/MMA8452Q.pdf